HW 4: C'mon Let's Link-ed List
Due: Tue, Nov 12 2024 at 9:00 PM EST
Released: Wed, Nov 6 2024
The goal of this assignment is to get some more practice writing recursive methods, as well as to get some practice with object-oriented programming concepts like inheritance.
Setup
The Assignment
Tim is working on his speech for his next talk. After all, the grind never stops. He doesn’t trust Google Docs and needs your help to create his very own, simplified document editing and sharing system to prevent his speech from falling into the wrong hands.
Section 1: Linked lists
We’ve provided you with a simple linked list implementation in linkedlist.py. This is the implementation we discussed in class, with a few modifications. You will be adding a few methods to this implementation.
Part 1: Adding a remove method
Task 1: Implement a remove method in the LinkedList class that takes in an index and removes the item at that index from the list. The method should return the item that was removed. If the index is out of bounds, the method should raise an Exception. Look at the nth method for an example of how to raise an Exception.
Note: You should implement remove using a recursive helper method called
remove_from. Think about what the base case and recursive case should look
like!
The image below helps illustrate what the remove method should achieve. We have the linked-list [a,b,c,d] and
we want to remove the item at the 2nd index. The result would be linked list [a,b,d] pictured below with the pre-removal list.
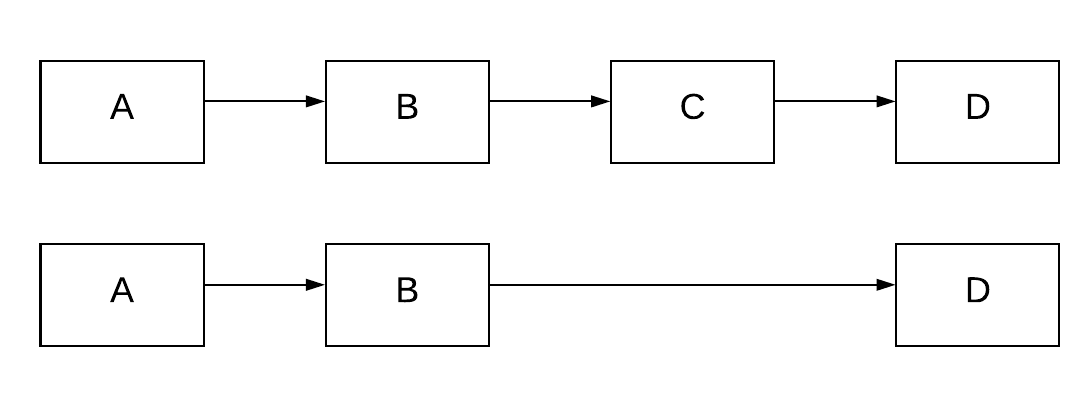
Task 2: Write tests for the remove method in test_linkedlist.py. Make sure to test for exceptional cases and edge cases.
Part 2: Optimizing the length method
Right now, the length() method runs in linear time in the length of the list, since it has to look at every node. Tim thinks this is too slow and wants you to optimize it.
Task 3: Modify the linked list implementation to reduce the time complexity of the length method.
Note: You don’t need to write or modify any tests for this part of the
assignment. Once you’ve fixed all of the methods, our test suite (as well as the
tests you wrote for remove) should pass.
Hint: Using count!
We can do this more efficiently by adding a field called count to the LinkedList class. This field should be updated whenever we add or remove an element from the list. This way, we can return the value of count in constant time.
This should be a simple change to the __init__, append, and remove methods. You should also update the length method to return the value of count.
Section 2: Cloud-based Document Editing and Sharing System
We’d like you to implement a (very) simplified version of the logic for a cloud-based document editing and sharing system (like Google Docs). You’ll implement two classes that handle document creation and permissions.
Part 3: Implementing the User and AdminUser classes
Take a look at the Document class in docs.py. This class represents
individual documents, which have:
- a name
- contents (i.e., text)
- a creator ID
- a list of user IDs who can access the document
Task 4: Implement a simplified cloud-based document editing and sharing system with two classes: User and AdminUser.
Part 3.1: User Class
You should implement a User class that has the following methods:
__init__(self, user_id: int)create_document(self, name: str, contents: str) -> Nonecan_access(self, doc: Document) -> boolget_document(self, index: int) -> Document
__init__
The __init__ method should take in a user id (an integer). It should
initialize two fields: a user_id field that records the user’s ID and a
documents field that holds an (initially empty) list of the documents the user
has created.
create_document
The create_document method should take in the name and contents of a
document. It should create a new document (i.e., a new instance of the
Document class) and add it to the user’s list of documents. The constructor
for the Document class takes a user ID; you should pass in the user’s ID for
that argument.
can_access
The can_access method takes in a Document and returns a boolean. It should
check whether the user’s ID is in the set of users who can access the document
(which you can get with doc.user_ids_with_access()).
get_document
The get_document method takes in the index of a document and returns that
document (i.e., looks up that index in the user’s documents list). If there is
no such document in the list, your method should raise a NoDocumentError.
Part 3.2: AdminUser Class
Then, create an AdminUser class that inherits from User:
- Do not implement
__init__for AdminUser. - Override
can_accessto always return True.
can_access
Admin users should be able to access any document, so this method should always
return True. It should have the same signature as the can_access method on
the User class.
Part 4: Testing
Task 5: Write tests for the User and AdminUser classes in test_docs.py. Make sure to test for exceptional cases and edge cases.
Remember to test all the methods you implemented in the User and AdminUser classes. You should test for cases where the user can access the document, where the user cannot access the document, and where the document does not exist. Can you think of any other edge cases to test?
Task 6: Expand the test suite for linked lists in test_linkedlist.py. We have provided you with a few tests, but you should add more to ensure that your implementation is correct.
Part 5: README
In your README.txt, please include answers to the following questions:
- Did you discuss this assignment with any other students? Please list their cs logins.
- How many late days are you using on this assignment?
Submission
Handin the following files to gradescope when submitting the assignment:
linkedlist.pytest_linkedlist.pydocs.pytest_docs.pyREADME.txt
Please don’t put your name in your code files, as we grade anonymously. If you have any questions about the assignment, please post on Ed.
You can only use a maximum of 3 late days per assignment. If the assignment is late (and you do NOT have anymore late days) no credit will be given.